As a consequence of the global pandemic, uncertain economic environment, wars, inflation and labour shortages, it has become increasingly challenging for businesses to remain competitive. So in this blog, we explain what is workforce optimization and how it works, we explain how it can increase your revenue, how it can help you remain competitive, as well as the other benefits that you can expect from it.
Workforce optimization is an approach to workforce management that seeks to optimise staffing levels to meet customer demand. The strategy involves automating processes, data visibility, compliance with legislation and solving business problems related to staffing. The objective is often described as “right people, right place, right time”
How does workforce optimisation work?
There are three key phases to workforce optimization.
- Forecasting: an accurate forecast of the variable that impacts demand over time. Often called a time series forecast and often generated by AI.
- Build a demand curve: A prediction of how many staff, by role type by hour, are required to ensure that the forecasted sales are met or maximised.
- Schedule staff: The allocation of those staff to shifts or tasks in an optimal way, taking into account the demand curve plus other factors such as compliance, budget, and staff preferences.
How do the three phases of workforce optimisation work?
In practice, these three steps are best achieved using AI inputs into workforce management software. The AIs will outperform a manager with a spreadsheet and can scale much quicker. Here is how each works:
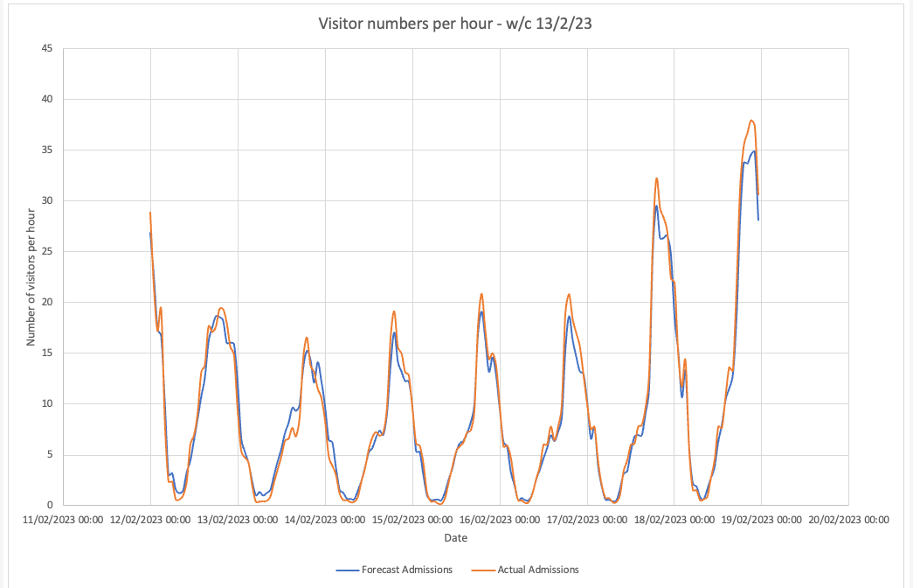
Forecasting: A forecast is a prediction of the variables that impact demand. Below is an example of an AI-generated forecast of visitor numbers for a single venue. Often there will be a number of forecasts required – for example, you might want to predict the number of visitors, revenues, number of items sold, number of transactions or “baskets”. The AI will need to generate each of these forecasts for every department in every venue that your company operates. Often that could be several hundred forecasts required. They are often delivered two to three weeks in advance to allow for the staff to be given their schedules in plenty of time.
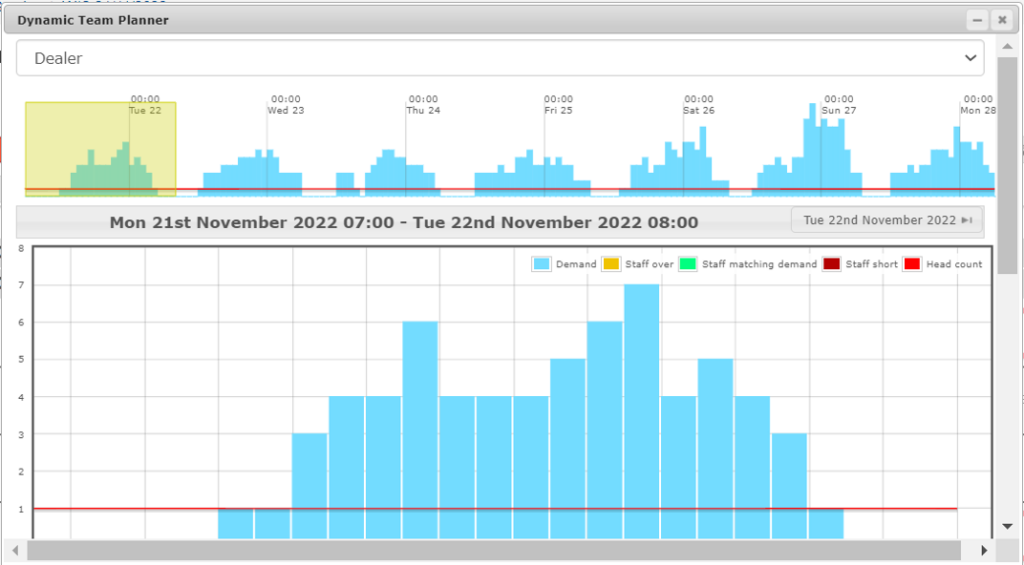
Building a demand curve:
Once all of the forecasts are available, these are fed into a second AI, which predicts the number of staff required to deliver the expected sales. Below is a 7-day demand forecast for a role by the hour. It shows how many employees in that role are needed each hour. This is then published to a workforce management system via an API.
The AI building the demand forecast takes into account a number of factors, these include:
- The sales forecasts
- Historic staffing levels against a given level of sales.
- Minimum and maximum staffing levels
- Regulatory and other operational requirements.
Scheduling: This is the process of building the optimal rota to meet the demand curve built in the previous step. However, this has to take into account many other factors, such as staff preferences, compliance and staff contracts. We have written a number of other blog articles on AI-powered auto-scheduling, which you might find helpful.
Why should I use workforce optimisation?
It’s pretty simple to maximise revenue for a given resource.
How can workforce optimisation generate more revenue for me?
We hope that you have a good understanding of what is workforce optimization so far, and now we want to explore how it can generate more revenue for your business.
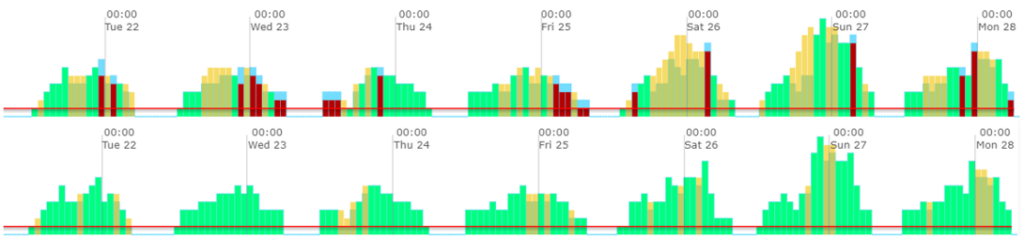
The below image is an example of a demand curve showing, on the top row, a 7-day rota built by a workforce manager and on the bottom row, the same rota built by an AI.
Both rotas use the same level of staffing and therefore cost the same to operate. In this case, the forecasts and the demand curve were both generated by an AI and are the same, so the only difference is the method of employee scheduling.
In the software being used, green indicates the correct number of staff have been allocated, and red indicates too few and yellow indicates too many. You can see that the AI has done a much better job of the resource allocation, and this will show at the tills. The red sections of the demand curve are likely to lead to queues and bad service, and the yellow ones are wasted resources and excess costs. These curves clearly illustrate the revenue-generating capability of AI-powered workforce optimisation.
What are the benefits of workforce optimisation?
The benefits aren’t just limited to revenue generation; a good workforce optimisation process has many other benefits.
- Meets demand: does your employee schedule have the right number of employees working at the right time with the right skills to meet your customer demand?
- It is fair: are all unpopular shifts evenly distributed? Do all staff get a fair share of overtime or hours worked?
- It is compliant: does each shift meet Working Time Directive rules and any local agreements you have with your employees?
- Cost-effective and on budget: is your employee schedule as cost-effective as possible?
- Covers tasks: do you have sufficient resources and skills on site to do all of the tasks that are required during that shift?
- Supports time off: the employee schedule should support and honour their booked time off.
- It takes into account staff availability and preferences: a good employee scheduling software will avoid scheduling staff when they can’t work and try to avoid scheduling them when they would prefer not to work.